HIC
70
INTRODUCTION TO TSKgel HIC COLUMNS
Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) is based on the
interaction between hydrophobic groups on a protein and a hydrophobic
ligand on the solid support. HIC offers a distinct advantage for easily
denatured proteins; it can be run using moderate concentrations of
ammonium sulfate, which favors the stability of many proteins.
The binding of proteins to a hydrophobic matrix is affected by a
number of factors including (1) the type of ligand, (2) the ligand density
on the solid support, (3) the backbone material of the matrix, (4) the
hydrophobic nature of the protein, and (5) the type of salt used. All of
these factors help to make HIC a powerful technique for the separation
of biomolecules.
Tosoh Bioscience offers three different HIC column types in analytical
format: TSKgel Phenyl-5PW, Ether-5PW and Butyl NPR. TSKgel Phenyl-
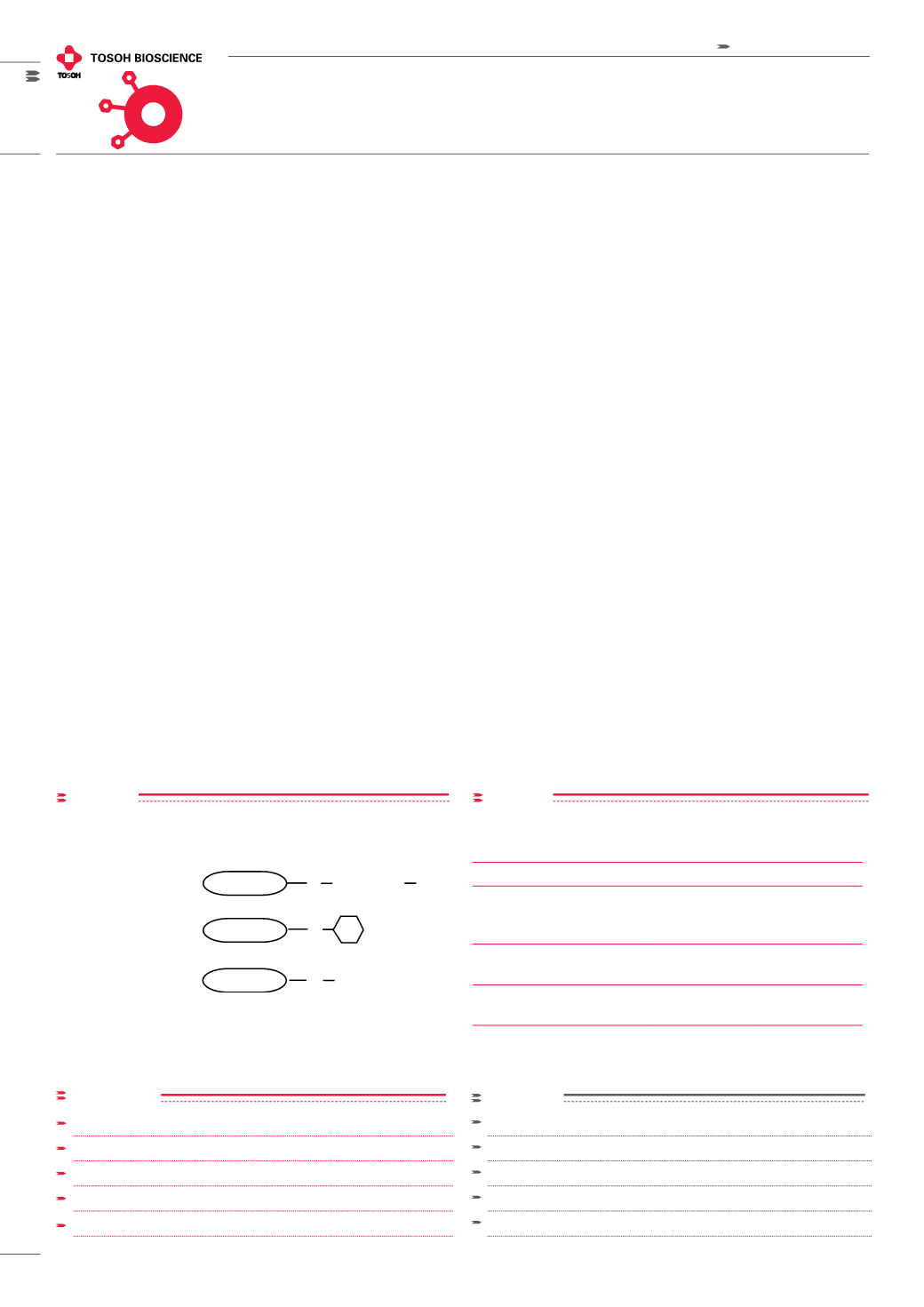
5PW is also available in preparative column formats. See
Figure 1
for
the structure of the HIC resins.
Column Selection
TSKgel HIC stationary phases are polymethacrylate-based with a
choice of three ligands with varied hydrophobicities from low to high.
TSKgel Ether-5PW and Phenyl-5PW are based on a porous base matrix
with 100 nm pores and available with various particle sizes depending
on column dimensions, while TSKgel Butyl-NPR is based on a 2.5 µm
nonporous base particle. Nonporous resins (NPR) re typically used for
high-speed analytical applications.
TSKgel Ether-5PW
is less hydrophobic than TSKgel Phenyl-5PW. It
displays weaker interaction and thus shorter retention times compared
to Phenyl-5PW.
TSKgel Ether-5PW is the best choice for the separation of very
hydrophobic proteins such as membrane proteins or monoclonal
antibodies.
The
TSKgel Phenyl-5PW
columnswere the first commercially available,
polymer-based columns for high performance HIC. These columns have
been instrumental to the increase in popularity of this technique for
analytical, preparative, and process scale separations of biopolymers.
TSKgel Butyl-NPR
is the least hydrophobic among the three TSKgel
HIC columns and requires a higher salt concentration for binding. TSKgel
Butyl-NPR columns provide fast and quantitative HIC, because smaller
particles provide higher efficiency. By packing the 2.5 µm nonporous
resin particles into shorter columns, typical analysis times are reduced
to less than 10 minutes. Pore diffusion is often the rate-limiting step
in the overall mass transport of large biomolecules through a porous
column. Eliminating the pores provides higher resolution at higher
flow rates. Another benefit of NPR resins is excellent mass recovery,
allowing quantitation down to nanogram levels. These properties make
TSKgel Butyl-NPR the preferred choice for process monitoring and
quality control. TSKgel Butyl-NPR is getting increasingly popular for
the analysis of antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) and is available in two
dimensions: 3.5 cm length for high throughput and 10 cm length for high
resolution.
TSKgel HIC columns are compatible with water soluble organic solvents
at concentration below 50 % (20 % for Butyl-NPR).
FEATURES
BENEFITS
Choice of three hydrophobic ligands (ether, phenyl or butyl)
Added flexibility during method development
Rigid polymeric base resin
Wide pH range (2-12) enabling robust cleaning options
Similar chemistry to TOYOPEARL resins
Seamless scalability from analytical to preparative scaley
TSKgel Phenyl-5PW offered in PEEK hardware
Eliminates undesirable interactions with column hardware
Ether and Phenyl available in 2 mm ID format
LC-MS applications
figure 1
Structure of TSKgel HIC resins
Structure of TSK-GEL HIC resins
5000PW (CH
2
CH
2
O)
n
H
TSKgel Ether-5PW
NPR
CH
2
CH
2
-CH
2
-CH
3
TSKgel Butyl-NPR
TSKgel Phenyl-5PW 5000PW O
O
O
O
Sample
MW range (Da) TSKgel Column
Peptides
< 10,000
Butyl-NPR
Medium to large proteins
> 10,000
Phenyl-5PW
Ether-5PW
Butyl-NPR
DNA, RNA, and PCR products > 500,000
Phenyl-5PW
Butyl-NPR
Oligonucleotides
> 10,000
Phenyl-5PW
Butyl-NPR
TABLE I
Column selection for the TSKgel HIC columns


