20
IEC
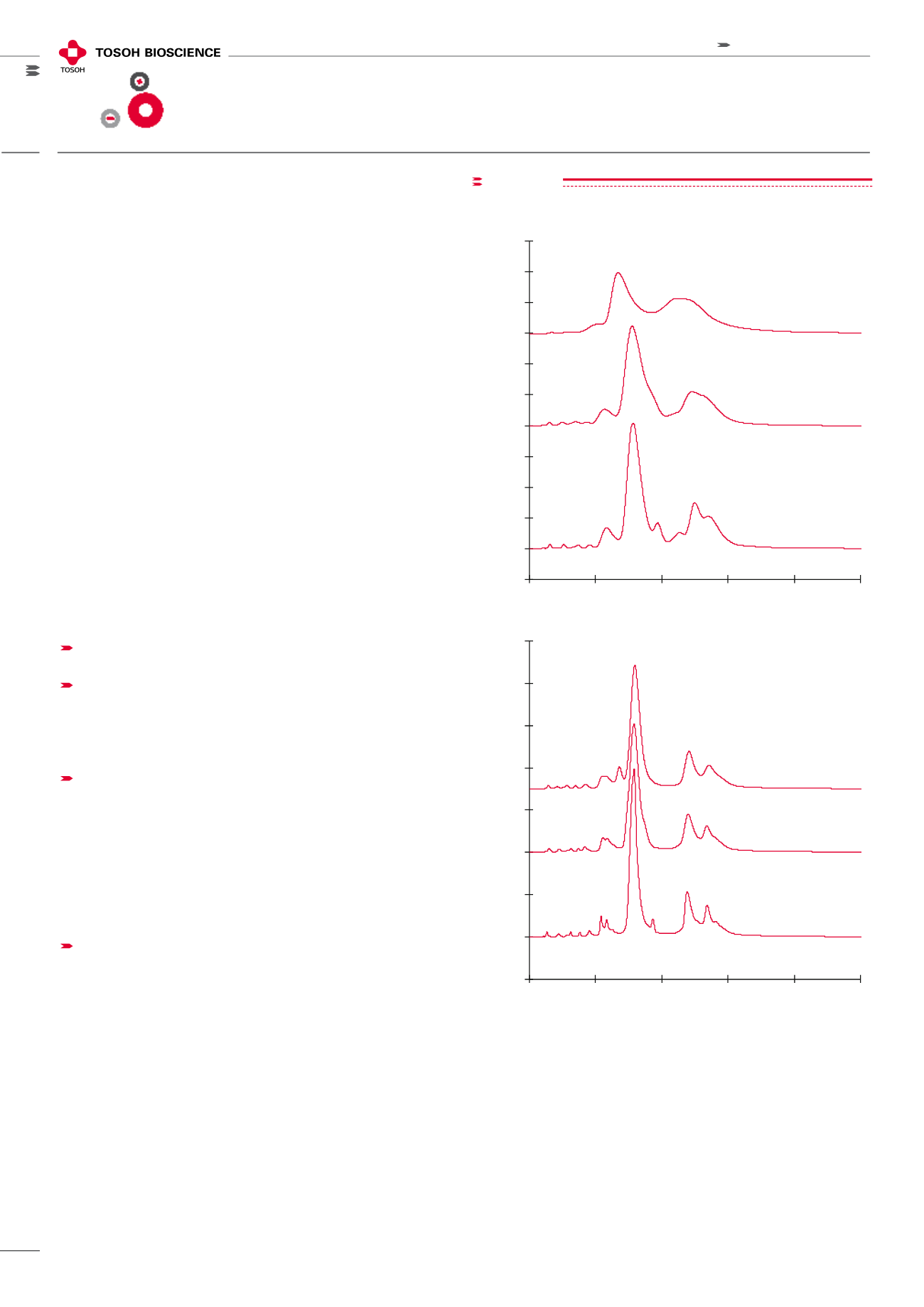
Multiple particle sizes simplify scaling up or
down
Because TOYOPEARL HW-65 and TSKgel products have
similar backbone chemistry and selectivity, scaling up or
scaling down for a selected ion exchange method is simple.
Practically speaking, the chromatographic conditions that
work for one particle size will work for all particle sizes
with a given ligand functionality. The elution order of the
components will remain the same with increasing
resolu-
tion as the particle size gets smaller (Figure 3). Figure 4 lists
the complete range of ion exchange products, particle sizes
and suggests how they are typically placed into a manu-
facturing scheme. The availability of smaller bead sizes for
greater resolution while maintaining the same selectivity
is particularly useful in the areas of oligonucleotide and
peptide purification.
Resin physical property selection
For resins available in different pore sizes with the same
ligand and ligand attachment chemistry.
For bind/elute chromatography:
Select the smallest pore size resin appropriate for the
size of the target molecule.
Select a larger particle size for a capture step, a smaller
one for intermediate or polishing steps.
For flow through chromatography:
If the target molecule’s size is larger than most
components of the feedstream, select a pore size which
will tend to exclude it (known as kinetic exclusion, this
technique can also be used under binding conditions as
the excluded molecule only sees 1% of the resin surface
area and the capacity/recovery loss is minimal).
For large molecule impurity clearance:
Select a pore size which includes the target molecule,
but excludes
the impurity (see the calibration curves of
the TOYOPEARL base beads in the SEC section of the
catalog as an aid).
Ion exchange
chromatography
figure 3
-0.05
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
0.50
0
10
20
30
40
50
UV 280 nm
Elution time (min)
mAb
TSKgel SuperQ-5PW resins
C (100 µm)
M (65 µm)
S (35 µm)
30 µm
20 µm
10 µm
Toyopearl SuperQ-650 resins
Resins:
1) Toyopearl SuperQ-650C (100
µ
m)
2) Toyopearl SuperQ-650M (65
µ
m)
3) Toyopearl SuperQ-650S (35
µ
m)
4) TSKgel SuperQ-5PW(30) (30
µ
m)
5) TSKgel SuperQ-5PW(20) (20
µ
m)
6) TSKgel SuperQ-5PW (10
µ
m)
Column size:
7.5mm ID x 7.5cm
Mobile phase:
Buffer A: 0.02mol/L Tris-HCl, pH 8.5
Buffer B: 0.5mol/L NaCl in Buffer A
Gradient:
60 min linear gradient from Buffer A to Buffer B
Flow rate:
136cm/hr (1.0mL/min)
Detection:
UV @ 280nm
Sample:
mAb in mouse ascites (dilution, x 5)
Sample vol.:
100
µL
-0.10
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
0.60
0.70
0
10
20
30
40
50
UV 280 nm
Elution time (min)
mAb
Scale up or down using the same ligand
Resins: 1) TOYOPEARL SuperQ-650C (100 µm); 2) TOYOPEARL SuperQ-650M
(65 µm); 3) TOYOPEARL SuperQ-650S (35 µm); 4) TSKgel SuperQ-5PW(30)
(30 µm); 5) TSKgel SuperQ-5PW(20) (20 µm); 6) TSKgel SuperQ-5PW (10 µm)
Column size: 7.5 mm ID x 7.5 cm; Mobile phase: Buffer A: 0.02 mol/L
Tris-HCl, pH 8.5; Buffer B: 0.5 mol/L NaCl in Buffer A;
Gradient: 60 min linear gradient from Buffer A to Buffer B; Flow rate:
136 cm/h (1.0 mL/min); Detection: UV @ 280 nm;
Sample: mAb in mouse ascites (dilution, x 5); Sample vol.: 100 µL
SCALE UP OR DOWN USING THE SAME LIGAND


