38
Mx
TOYOPEARL Resins for Mixed-Mode Chromato-
graphy
Multimodal or mixed-mode chromatography denotes a
quite heterogeneous segment of liquid chromatography.
In general this term is used when a stationary phase of-
fers different modes of chromatography, modulated by the
properties of the mobile phase. In bioprocess chromatog-
raphy this term is most often used when ion exchange (IEX)
and hydrophobic interaction (HIC) are combined in one res-
in. Depending on the nature of IEX ligand – anion exchange
versus cation exchange – there are currently two versions
of mixed mode process resins on the market: multimodal
hydrophobic cation exchanger and hydrophobic anion ex-
changer. Multimodal or mixed-mode chromatography ex-
pands the range of chromatographic modes applied in bio-
purification and offers new selectivity options and a higher
salt tolerance than traditional ion exchange media. The
new TOYOPEARL MX-Trp-650M belongs to the category of
multi-modal cation exchangers. It uses tryptophan as the
active ligand (Figure 1). This amino acid has both weak car-
boxyl cation exchange and indole hydrophobic functional
groups. The selectivity of the resin can be adjusted through
control of binding or elution pH, ionic strength, salt type
and additives.
How does mixed mode chromatography work?
Depending of the nature of the mobile phase the interaction
of the proteins and the stationary phase is dominated by
either hydrophobic interactions (e.g. at high salt concentra-
tions) or by ionic interactions. The ionic and hydrophobic
properties of the multimodal ligand vary with salt concen-
tration and pH. Thus optimization of the eluents for adsorp-
tion, wash steps and elution is crucial.
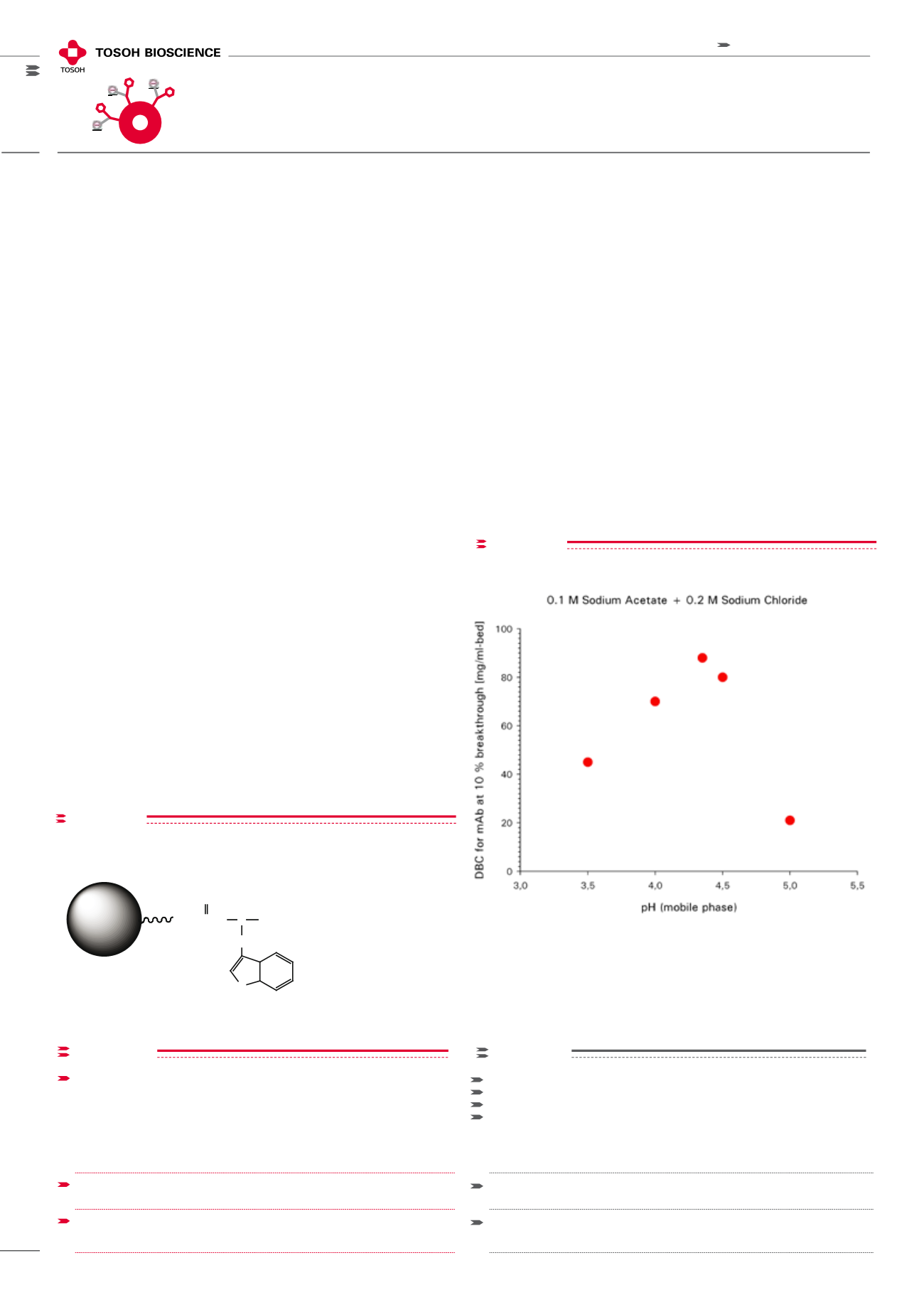
The binding capacity of TOYOPEARL MX-Trp-650M greatly
depends on pH (Figure 2). Buffer solutions with a pH
approximately two pH units beneath the isoelectric point
of the target molecule may serve as a first starting point
for screening binding conditions. However it is not recom-
mended to use a loading buffer pH below pH 3.0, as the
capacity does not inversely correlate to pH but achieves a
maximum at a specific pH, depending on the target protein.
Further, very low pH values may accelerate oxidation of
the resin. Besides the pH, the applied salt concentration
has a major impact on resin capacity. In a first approach,
the overall salt concentrations may range from 0.1 mol/L
to 0.3 mol/L. We suggest applying a concentration of 0.1
mol/L of the buffer salt with an addition of sodium chloride.
However, the salt dependency of DBC is varying depending
on the target molecule.
features
Benefits
Multimodal cation exchange resin
Selectivity adjustable by pH, salt type and ionic strength
Tolerates high conductivity feedstocks
High binding capacities for IgG and other proteins
Can be used for processing of clarified feedstocks at physi-
ological salt concentrations as well as for intermediate and
polishing applications
Fast mass transfer kinetics
Sharp elution peaks with mild conditions
High mechanical stability
Excellent flow characteristics in large columns
OCH
2
CNH
O
H
C COONa
N
H
CH
2
Weak cation exchange
Hydrophobic
TOYOPEARL
Product name: TOYOPEARL MX-Trp-650M
Particle size: 50-100 µm
TOYOPEARL MX-Trp-650M STRUCTURE
figure 1
INFLUENCE OF pH VALUE ON IgG dynamic binding capacity
Column size: 6.6 mm ID x 2.2 cm; Binding buffer: 0.1 mol/L ac-
etate buffer (pH 3.5 - 5.0) + 0.2 mol/L NaCl; Linear velocity: 150 cm/h;
Detection: UV @ 280 nm; Sample: humanized monoclonal IgG
Dynamic binding capacity (DBC) calculated at 10 % breakthrough.
figure 2
Mixed-mode
chromatography


