TSKgel® Amide-80 HILIC columns – for HPLC and UHPLC analyses
The Amide-80 is group of hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) columns available with various particle sizes (2-10 µm) and dimensions. The columns are established in glycan analysis, separation of oligonucleotides and peptides but have also proven in oligosaccharide and vitamin analysis. Due to low bleeding the separation can easily be connected to mass spectrometry analyses. The 2 µm version is designed for UHPLC applications whereas larger particles are used with HPLC systems and simplify HPLC-UHPLC transfer. As TSKgel Amide-80 columns can be used with 100 % organic solvents, they alternatively serve as normal phase columns.
| Base material: |
Silica |
| Particle size: |
2, 3, 5 or 10 µm |
| Pore size (mean): |
80 Å |
| Separation mechanism: |
Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) |
| Functional group: |
Carbomoyl |
| pH stability: |
2.0-7.5 |
| Organic concentration: |
0 – 100% |
| Temperature: |
10-80 °C (50 °C for 2 and 3 µm particles) |
| USP column compatibility: |
USP L68 |
Functional group of TSKgel Amide-80 columns
|
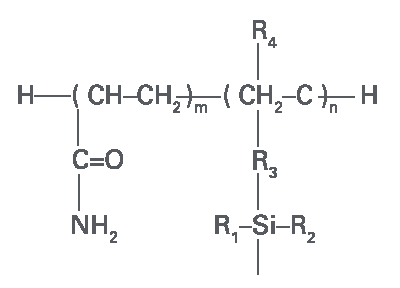 |
| Carbomoyl Group |
Benefits of Amide-80 columns – Durability, Speed
The high quality of Amide-80 HIlIC columns is visible in their long lifetime: in > 1000 injections, performance parameters such as theoretical plate numbers and asymmetry only slightly decreased by 5-6 %.
Durability of TSKgel Amide-80 columns (3 µm)
|
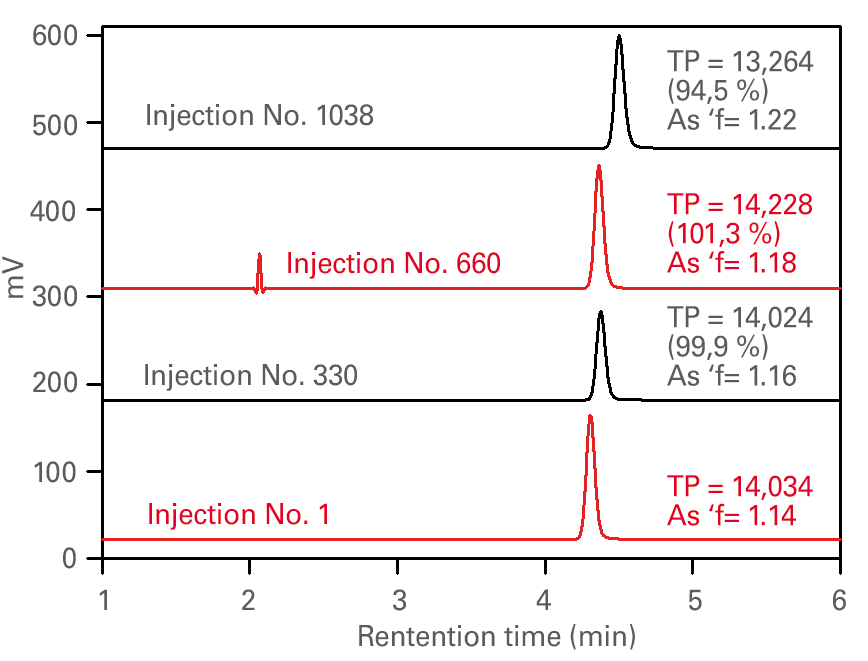 |
Separation of Uracil (37 mg/L) on TSKgel Amide-80 (3 µm, 2 mm ID x 15 cm L).
Mobille phase: H2O/ACN = 15/85
Flow rate: 0.2 mL/min
Injection volume: 2 µL
Detection: UV@254 nm
|
The many available dimensions and particle sizes of these HILIC columns allow you to smoothly adapt your analytics to new requirements: from analytical to semi-preparative applications, from standard HPLC to low inner diameters for a better combination of mass spectrometry or to ultra-fast UHPLC separations.
In the example shown below, the analysis of an eight-molecule mixture was transferred from HPLC using a column with 3 µm particles, 3 mm internal diameter, and 15 cm length to UHPLC using a column with 2 µm particles and only 5 cm length. Baseline separation was achieved with both methods, but the UHPLC method was considerably faster, taking only 1 minute compared to 9 minutes for the HPLC method.
Ultra-fast HILIC analysis with Amide-80
|
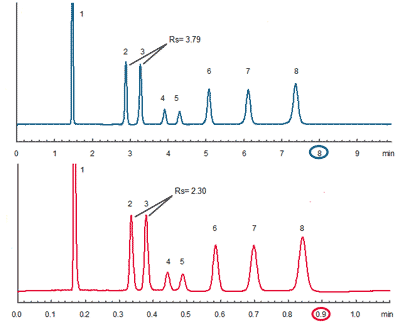 |
Top (HPLC): TSKgel Amide-80 (3 µm, 3 mm ID x 15 cm L), flow rate: 0.43 mL/min
Bottom (UHPLC): TSKgel Amide-80 (2µm, 3 mm ID x 5cm L)
Flow rate: 1.29 mL/min.
Mobile phase: 20 mmol/L NH4OAc (pH 4.7) / ACN = 10/90
Temperature: 40 °C; Injection volume: 2 µl
Sample: 1. Toluene (0.1 g/L), 2. Theophylline (0.1 g/L), 3. Theobromine (0.1 g/L), 4. NPβb-Glu (0.1 g/L),
5. Nαa-Glu (0.1 g/L), 6. 2’-deoxyuridine (0.1 g/L), 7. 5-methyluridine (0.1 g/L), 8. uridine (0.1 g/L) |
Application of the Amide-80 column – glycan analysis by HILIC-MS
Glycans are polysaccharide modifications in proteins impacting their function and thus need to be analyzed in the quality control of protein-based therapeutics. The gold standard method uses glycan structures that were released from the protein and labeled with a fluorophore for detection. The labelled glycans are separated by hydrophilic interaction chromatography as glycan patterns of different length and composition are differently hydrophilic. Best assignment of the glycan structure is achieved by adding mass spectrometry for exact mass determination of the peaks. The application note “UHPLC Glycosylation Analysis with TSKgel Amide-80 2 µm HILIC columns” shows how the column succeeds to separate mAb-released glycans for MS detection.
UHPLC-MS analysis of 2-AB labelled glycans released from human IgG
|
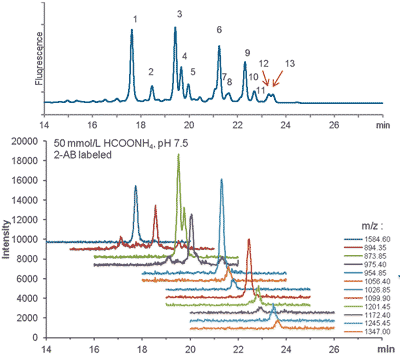 |
Column: TSKgel Amide-80 2 µm, 2.0 mm ID x 15 cm L
Mobile phase: A: 50 mmol/L HCOONH4, pH 7.5, B: ACN
Gradient: 75 % B (0-5 min), 75-50 % B (5-30 min linear)
Flow rate: 0.3 mL/min
Temperature: 40 °C
Detection: Top: fluorescence (ex @ 315 nm, em @ 380 nm)
Bottom: LC/MS ESI positive, SIM (Shimadzu LCMS-8030)
Injection vol.: 50 µl
Sample: 2-AB labelled glycans released from human IgG (Ludger) |